Indoor air pollution is a significant concern that often goes unnoticed. The air inside our homes can be more polluted than the air outside, posing potential health risks to ourselves and our loved ones. This post aims to shed light on common pollutants found in homes and provide effective solutions to combat indoor air pollution.
Common Pollutants Found in The Home
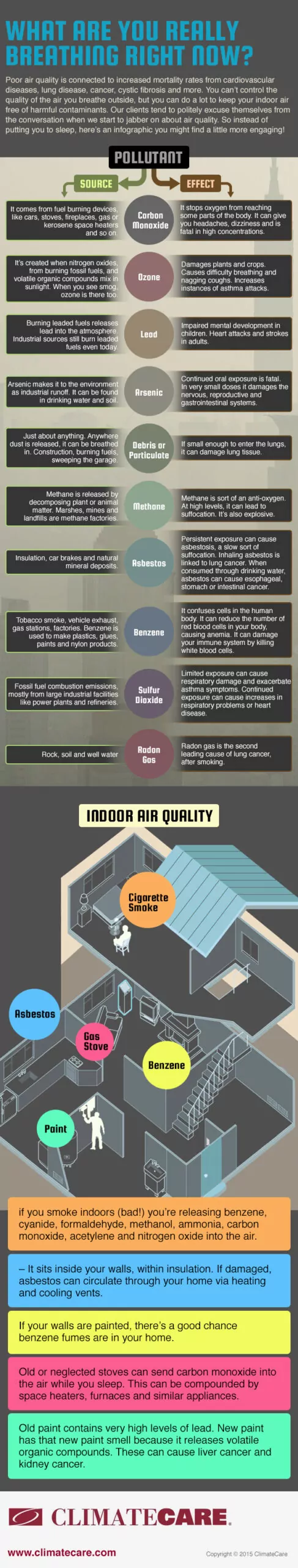
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless and odorless gas emitted from burning fuels such as gas, oil, and wood. Prolonged exposure can lead to headaches, dizziness, and even death.
Ozone
Ozone (O3) is a gas formed by the reaction of sunlight with pollutants like nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). While ozone high up in the atmosphere is beneficial, at ground level, it can cause respiratory issues and worsen existing lung conditions.
Lead
Lead can enter the home through old paint, dust, and contaminated soil. Exposure to lead can result in developmental delays, cognitive impairments, and other health problems, especially in young children.
Benzene
Benzene is a volatile organic compound found in tobacco smoke, household products, and vehicle emissions. Prolonged exposure to benzene can increase the risk of cancer and cause damage to the nervous system.
Arsenic
Arsenic can be present in water sources or building materials. Ingesting or inhaling high levels of arsenic can lead to skin issues, respiratory problems, and an increased risk of certain cancers.
Dust & Particulates
Dust particles containing allergens, pet dander, and pollen can trigger allergies and asthma symptoms, especially in individuals with respiratory conditions.
Methane
Methane is a greenhouse gas produced by natural gas leaks, waste decomposition, and certain industrial processes. High levels of methane contribute to climate change and can affect air quality.
Asbestos
Asbestos, commonly found in older homes, can release harmful fibres into the air when disturbed. Prolonged exposure to asbestos fibres can cause lung cancer and other serious respiratory diseases.
Sulphur Dioxide
Sulphur dioxide (SO2) is a gas emitted from burning fossil fuels, particularly coal and oil. Breathing in high concentrations of sulphur dioxide can irritate the respiratory system and worsen existing respiratory conditions.
Radon Gas
Radon gas is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can seep into homes through cracks in the foundation. Long-term exposure to radon increases the risk of lung cancer.
How to Get Rid of Indoor Air Pollution
To banish indoor air pollution and improve the air quality in your home, consider implementing the following solutions:
- Install carbon monoxide detectors and ensure proper ventilation.
- Use air purifiers to filter out harmful particles and allergens.
- Regularly inspect and remove sources of lead, such as old paint or contaminated soil.
- Minimize the use of products containing benzene and opt for natural alternatives.
- Test and treat water sources for arsenic contamination.
- Clean and dust surfaces regularly, and vacuum with a HEPA filter.
- Address natural gas leaks promptly and promote proper waste management.
- Seek professional help for asbestos removal or encapsulation.
- Reduce emissions by using cleaner energy sources and appliances.
- Test radon levels and install mitigation systems if necessary.
Wrap-Up
Indoor air pollution is a serious issue that requires attention and action. By understanding the common pollutants present in our homes and implementing effective solutions, we can create a healthier living environment for ourselves and future generations. Take the first step towards cleaner air and protect your loved ones with quality air purifiers from ClimateCare. Find your local HVAC supplier today!




